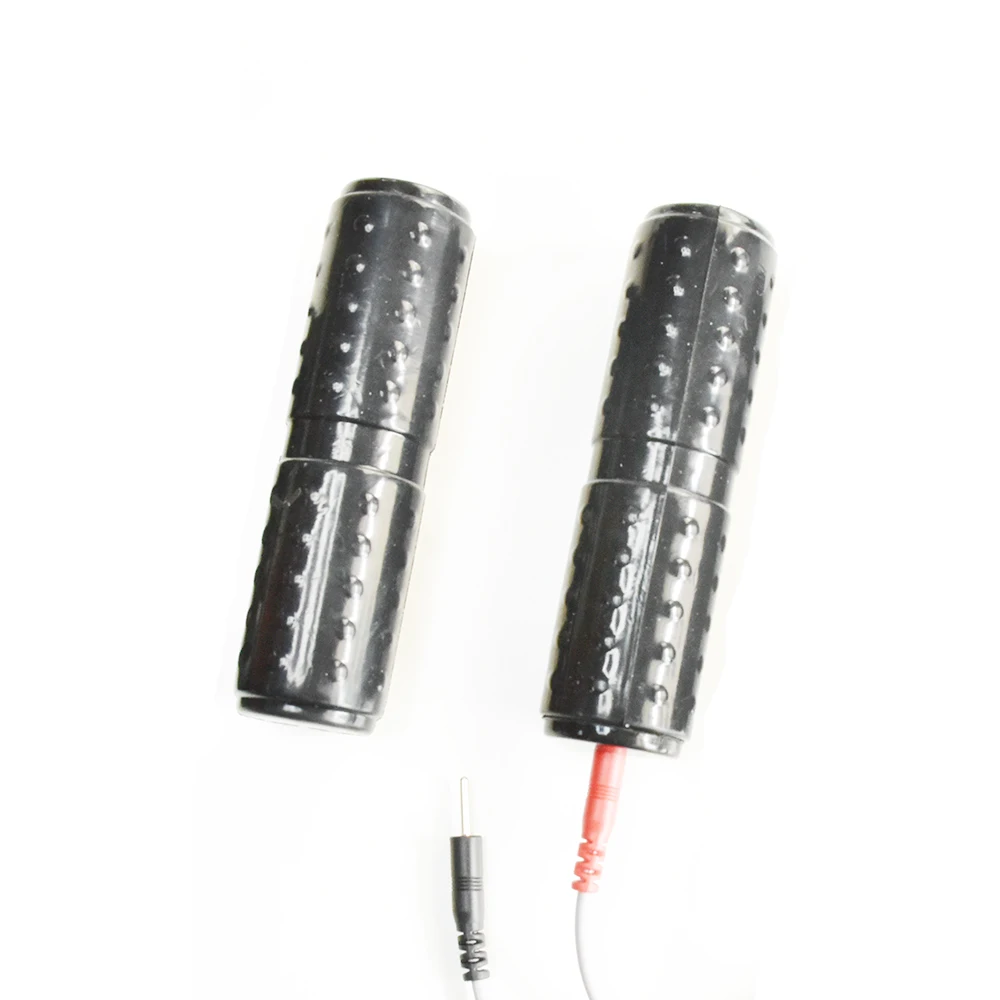
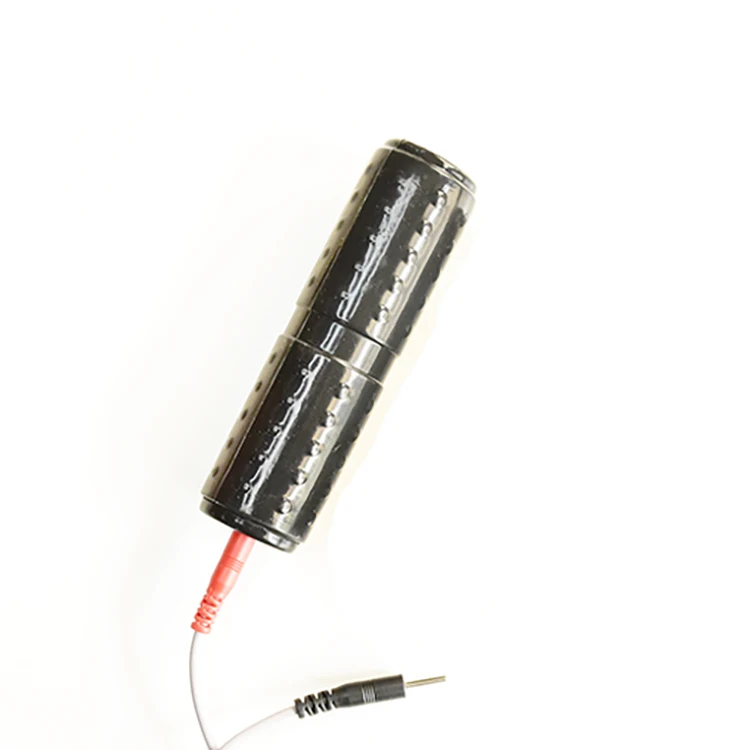
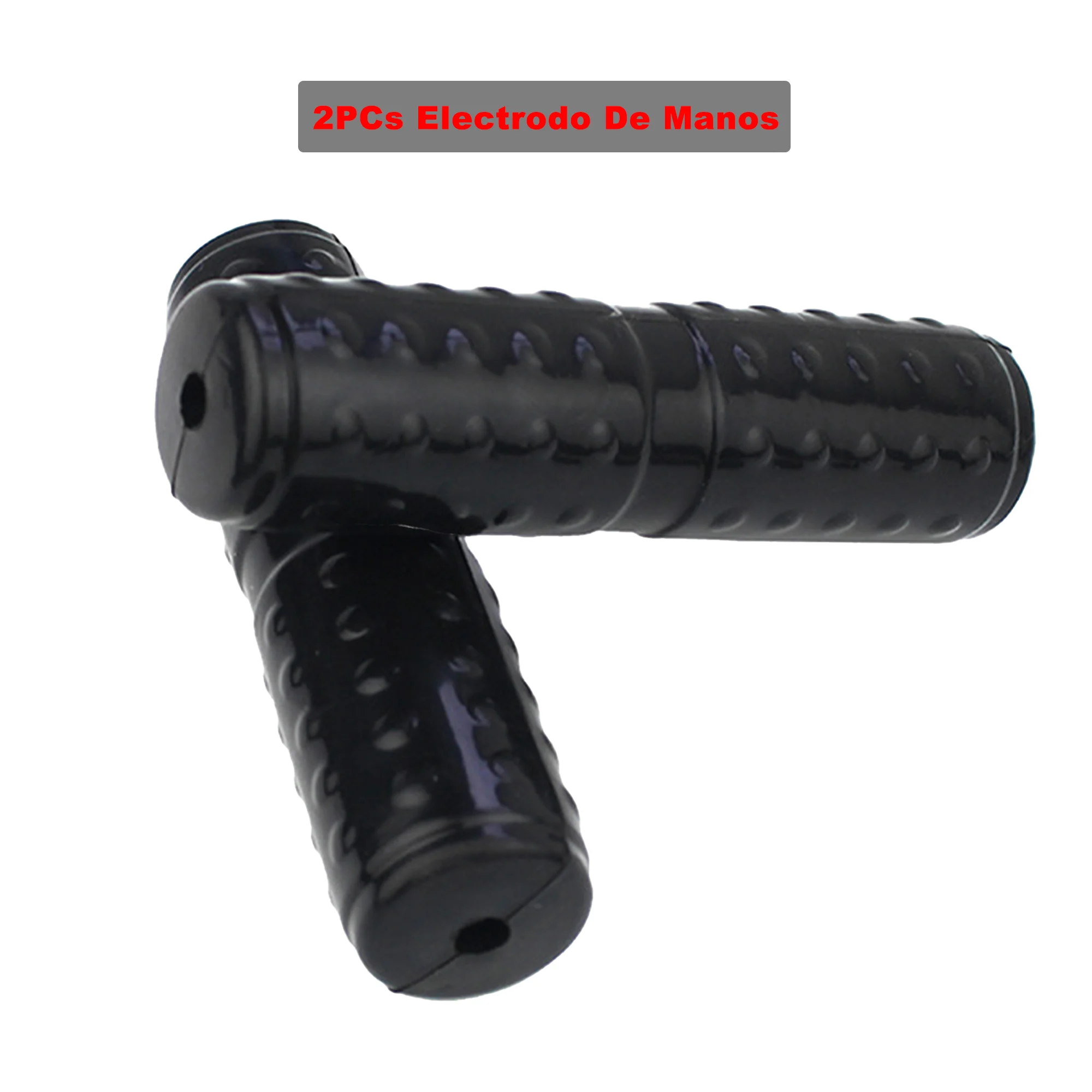
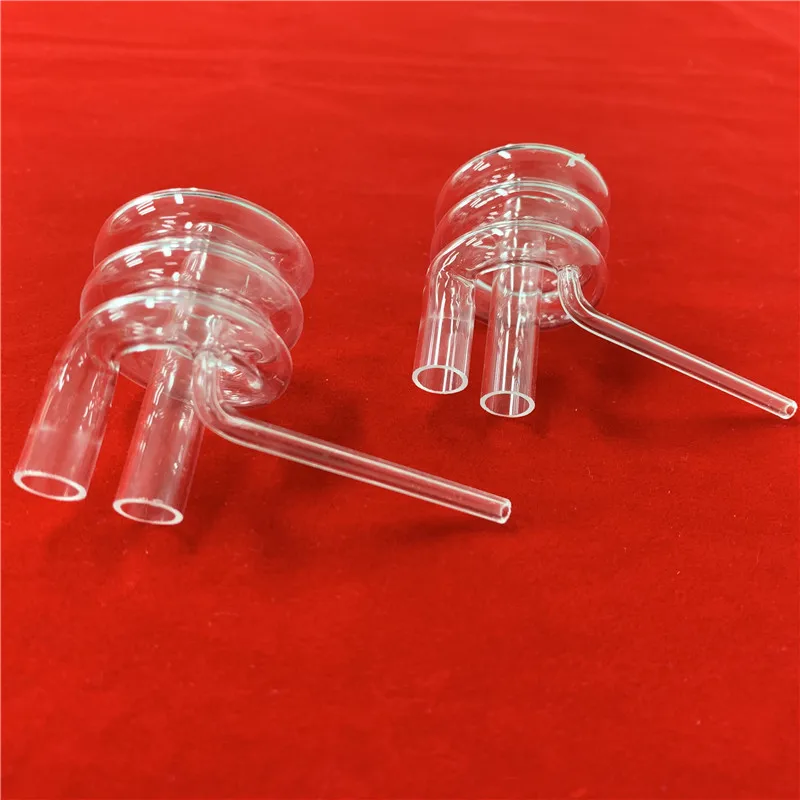
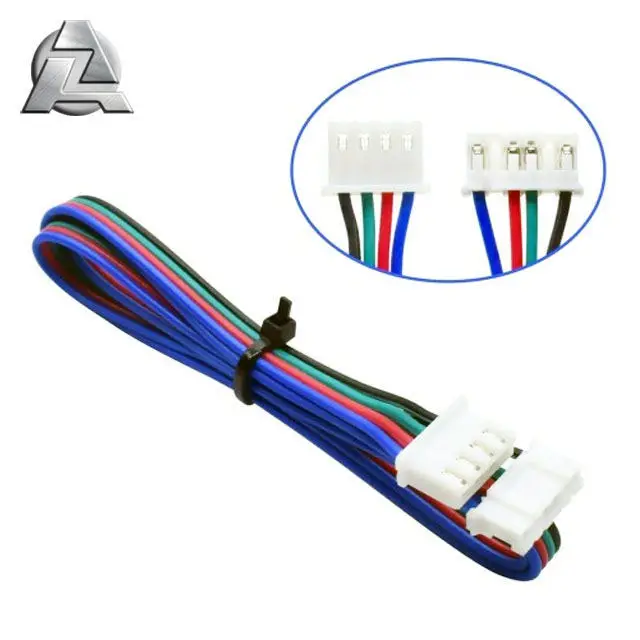
Accessory per Massaggio Elettrica Elettrodi Mano Adatto per Persone di et a Media 2x Hand/Palm Electrode For All TENS Machines
- Category: >>>
- Supplier: Guangzhou Roson Medical Devices Co. Ltd.
Share on (1601234793107):
Product Overview
Description
Factory view
Accessory per Massaggio Elettrica Elettrodi Mano Adatto per Persone di et a Media 2x Hand/Palm Electrode For All TENS Machines Pain Relief and Stress Reduction Electric Massager Electrotherapy and Stress Relief Physiotherapy Electrotherapy Hand Electrode for Electric Hands Electrode Massager for Electrotherapy Lightweight Hand Electrode TENS Machines Handheld Electric Massager



The functions of a hand-held electrode physiotherapy instrument typically encompass several aspects, aimed at providing
therapeutic benefits for various physical conditions. These functions often include:
1.Pain Relief: The instrument is commonly used for pain management, especially for muscular and joint pain. It can help in reducing chronic pain as well as pain from injuries.
2.Muscle Stimulation: It can stimulate muscles, which is beneficial for rehabilitating and strengthening muscles, particularly after an injury or surgery.
3.Improved Circulation: By stimulating muscles and nerves, these devices can enhance blood circulation, which is crucial for healing and maintaining muscle tissue health.
4.Reduced Inflammation: Regular use can lead to a reduction in swelling and inflammation, particularly in joint areas such as the knees, elbows, and back.
5.Relaxation and Stress Reduction: The stimulation can also help in relaxing muscles and reducing stress, which is beneficial for overall well-being.
6.Nerve Stimulation: For those suffering from nerve disorders or damage, these instruments can provide nerve stimulation that may aid in nerve function and healing.
7.Enhancing Range of Motion: It can assist in improving flexibility and range of motion, which is particularly useful for
individuals recovering from injuries or dealing with conditions like arthritis.
8.Edema Reduction: The instrument can help in reducing edema or fluid retention in limbs, a common issue after injuries or surgeries.
Each device may have specific features and settings tailored to different therapeutic needs, so it's important to consult with a healthcare provider for the most effective use.
2.Muscle Stimulation: It can stimulate muscles, which is beneficial for rehabilitating and strengthening muscles, particularly after an injury or surgery.
3.Improved Circulation: By stimulating muscles and nerves, these devices can enhance blood circulation, which is crucial for healing and maintaining muscle tissue health.
4.Reduced Inflammation: Regular use can lead to a reduction in swelling and inflammation, particularly in joint areas such as the knees, elbows, and back.
5.Relaxation and Stress Reduction: The stimulation can also help in relaxing muscles and reducing stress, which is beneficial for overall well-being.
6.Nerve Stimulation: For those suffering from nerve disorders or damage, these instruments can provide nerve stimulation that may aid in nerve function and healing.
7.Enhancing Range of Motion: It can assist in improving flexibility and range of motion, which is particularly useful for
individuals recovering from injuries or dealing with conditions like arthritis.
8.Edema Reduction: The instrument can help in reducing edema or fluid retention in limbs, a common issue after injuries or surgeries.
Each device may have specific features and settings tailored to different therapeutic needs, so it's important to consult with a healthcare provider for the most effective use.
Products Description

**Benefits of hand-held electrode physiotherapy instrument**
Hochwertiges Elektrisch Leitendes Rubber Elektrisches Hand Electrode Massager

**How hand-held electrode Work with a TENS/EMS Device:**
Hand-held electrodes work with TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) and EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation) devices
by delivering electrical impulses from the device to specific areas of the body. These impulses help in pain management, muscle
stimulation, and rehabilitation. Here's how they function in conjunction with TENS and EMS devices:
Components:
1. **TENS/EMS Device**: The main unit that generates electrical impulses.
2. **Electrodes**: Conductive pads or hand-held devices that transfer the electrical impulses from the TENS/EMS device to the
body.
3. **Wires**: Connect the electrodes to the TENS/EMS device.
4. **Power Source**: Batteries or a power adapter that powers the TENS/EMS device.
by delivering electrical impulses from the device to specific areas of the body. These impulses help in pain management, muscle
stimulation, and rehabilitation. Here's how they function in conjunction with TENS and EMS devices:
Components:
1. **TENS/EMS Device**: The main unit that generates electrical impulses.
2. **Electrodes**: Conductive pads or hand-held devices that transfer the electrical impulses from the TENS/EMS device to the
body.
3. **Wires**: Connect the electrodes to the TENS/EMS device.
4. **Power Source**: Batteries or a power adapter that powers the TENS/EMS device.

Working Mechanism:
1. **Setting Up the Device**:
- **Power On**: Turn on the TENS/EMS device.
- **Adjust Settings**: Select the appropriate mode, intensity, and duration based on the treatment required.
2. **Connecting Electrodes**:
- **Attach Electrodes**: Connect the hand-held electrodes to the TENS/EMS device using the provided wires.
- **Placement**: Place the electrodes on the targeted area of the body. For hand-held electrodes, this might involve holding them
in specific positions.
3. **Electrical Impulse Generation**:
- **Impulse Creation**: The TENS/EMS device generates controlled electrical impulses.
- **Transmission**: These impulses travel through the wires to the hand-held electrodes.
- **Power On**: Turn on the TENS/EMS device.
- **Adjust Settings**: Select the appropriate mode, intensity, and duration based on the treatment required.
2. **Connecting Electrodes**:
- **Attach Electrodes**: Connect the hand-held electrodes to the TENS/EMS device using the provided wires.
- **Placement**: Place the electrodes on the targeted area of the body. For hand-held electrodes, this might involve holding them
in specific positions.
3. **Electrical Impulse Generation**:
- **Impulse Creation**: The TENS/EMS device generates controlled electrical impulses.
- **Transmission**: These impulses travel through the wires to the hand-held electrodes.



Product Specification
Item | Accessori Per Elettrodi Manuale Two Elektrisch Leitendes Rubber Handelektrodenzubehör |
Type | Adatto per persone di et à media |
Application | Hand, Foot, Feet |
Product Name | Hand Electrode Massager |
Function | Relieve hand tiredness fatigue,promote circulation |
Technology | Electrical stimulation |
Connection | 2.0mm Pin lead wire |
Material | TPU and conductive silica gel |
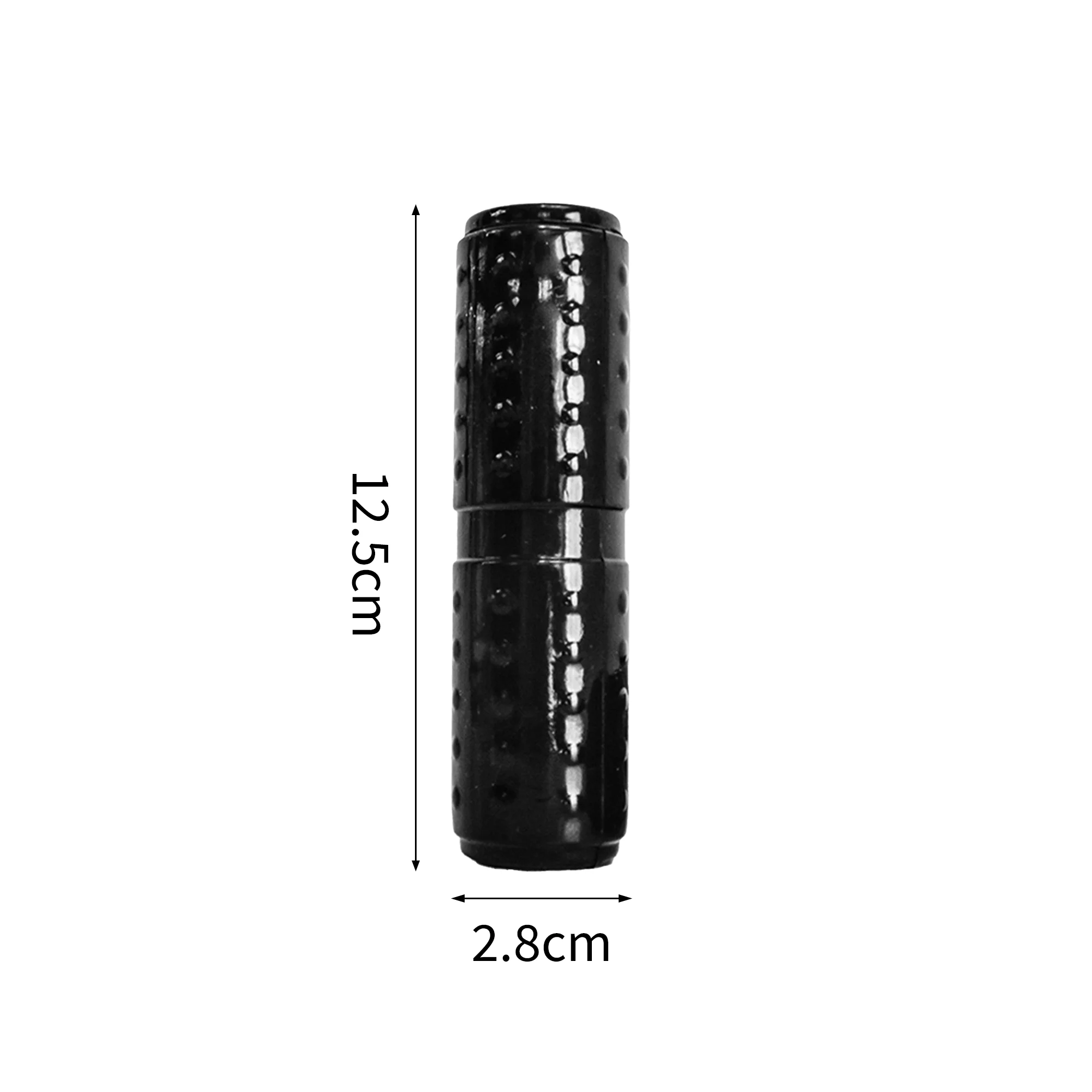
Net weight | 150 gram |
Size | Free-size |
OEM/ODM Service | Acceptable |
Recommend Products
Details Images





Exhibition
2015 China Import and Export Fair
The fair is divided into three phases, each focusing on different product categories:
* Phase 1: Electronics, home appliances, lighting, vehicles and spare parts.
* Phase 2: Consumer goods, gifts, and home decorations.
* Phase 3: Textiles and garments, shoes, office supplies, cases and bags, recreation products, and medical devices.
* Phase 2: Consumer goods, gifts, and home decorations.
* Phase 3: Textiles and garments, shoes, office supplies, cases and bags, recreation products, and medical devices.
2016 China Import and Export Fair
Participants: The fair attracts a large number of exhibitors and buyers from around the world. It provides a platform for Chinese
manufacturers and exporters to showcase their products and connect with international buyers.
manufacturers and exporters to showcase their products and connect with international buyers.
Product Categories: A wide range of products is exhibited, including electronics, machinery, hardware, textiles, clothing,
footwear, home goods, and much more.
footwear, home goods, and much more.
2017- HGH
Business Opportunities: The fair is not only a platform for showcasing products but also serves as a hub for business
negotiations, networking, and the establishment of trade partnerships.
negotiations, networking, and the establishment of trade partnerships.
Online Participation: In recent years, the fair has incorporated online elements, allowing participants to engage in virtual trade
shows, explore products, and conduct business negotiations remotely.
shows, explore products, and conduct business negotiations remotely.
2017 China Import and Export Fair
Phases: The fair is divided into three phases. The first phase usually focuses on electronics and household electrical appliances, the second phase on consumer goods, gifts, and home decorations, and the third phase on textiles and garments, shoes, office
supplies, cases and bags, recreation products, medicines, medical devices, and health products.
supplies, cases and bags, recreation products, medicines, medical devices, and health products.
2018 China Import and Export Fair
Exhibitors and Buyers: The Canton Fair attracts a large number of exhibitors and buyers from around the world. It provides a platform for Chinese companies to showcase their products to a global audience and for international buyers to connect with
Chinese suppliers.
Chinese suppliers.
2018 China Import and Export Fair
Product Categories: The fair covers a wide range of product categories, including machinery, electronics, hardware and tools, building materials, lighting, vehicles and accessories, chemicals, home decorations, textiles, garments, and more.
2018 China Import and Export Fair
Product Categories: The fair covers a wide range of product categories, including machinery, electronics, hardware and tools, building materials, lighting, vehicles and accessories, chemicals, home decorations, textiles, garments, and more.
2019 China Import and Export Fair
Online and Offline Presence: In recent years, the Canton Fair has embraced digital platforms to facilitate online exhibitions and virtual interactions, especially in response to global challenges such as the CO-VID-1-9 pandemic. This allows participants who are unable to attend in person to still engage with the fair.
2023 China Import and Export Fair
Global Impact: The Canton Fair is considered a barometer of China's foreign trade and has a significant impact on the global market. It serves as a platform for international trade and cooperation, promoting economic development and collaboration between Chinese and international businesses.
Why Choose Us

What is electrical therapy used to treat?
Electrical therapy, also known as electrotherapy, is used to treat a variety of medical conditions and can serve different
therapeutic purposes. The application of electrical currents for therapeutic effects can address pain, muscle dysfunction,
neurological conditions, and more. Here are some common uses of electrical therapy:
It's important to note that while electrical therapy can be beneficial for certain conditions, it may not be suitable for
everyone, and its effectiveness can vary from person to person. The specific type of electrical therapy, parameters of
stimulation, and treatment duration will depend on the individual's condition and the goals of therapy. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment approach for your specific needs.
therapeutic purposes. The application of electrical currents for therapeutic effects can address pain, muscle dysfunction,
neurological conditions, and more. Here are some common uses of electrical therapy:
1. Pain Management:
* Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): TENS is commonly used for pain relief. It involves the use of a device that delivers low-voltage electrical currents through electrodes placed on the skin, disrupting pain signals and providing relief for various types of pain, including chronic and acute conditions.
2. Muscle Stimulation and Rehabilitation:
* Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES): NMES is used to stimulate muscles, often in rehabilitation settings. It can help prevent muscle atrophy, improve muscle strength, and aid in the recovery of injured or weakened muscles.
3. Wound Healing:
* Galvanic Stimulation (GS): GS is sometimes used to promote wound healing. The application of direct current is believed to enhance blood flow and cellular activity, potentially accelerating the healing process.
4. Functional Rehabilitation:
* Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES): FES is employed to stimulate specific nerves and muscles to produce functional movements. It is often used in rehabilitation for individuals with neurological conditions, such as spinal cord injuries or stroke, to improve mobility and restore functional activities.
5. Reducing Inflammation:
* Certain forms of electrotherapy may have anti-inflammatory effects, contributing to the management of conditions involving inflammation.
6. Nerve Stimulation:
* Interferential Current (IFC): IFC involves the use of intersecting medium-frequency electrical currents. It can be used for pain relief, muscle stimulation, and improving blood flow by creating a modulating interference effect.
7. Skeletal Pain and Osteoarthritis:
* Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy (PEMF): PEMF involves the use of electromagnetic fields to improve circulation and reduce pain and inflammation. It is sometimes used in the management of musculoskeletal conditions, including osteoarthritis.
8. Urinary Incontinence:
* Transvaginal Electrical Stimulation (TES) or Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): Electrical stimulation may be used to strengthen pelvic floor muscles and improve symptoms of urinary incontinence.
* Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): TENS is commonly used for pain relief. It involves the use of a device that delivers low-voltage electrical currents through electrodes placed on the skin, disrupting pain signals and providing relief for various types of pain, including chronic and acute conditions.
2. Muscle Stimulation and Rehabilitation:
* Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES): NMES is used to stimulate muscles, often in rehabilitation settings. It can help prevent muscle atrophy, improve muscle strength, and aid in the recovery of injured or weakened muscles.
3. Wound Healing:
* Galvanic Stimulation (GS): GS is sometimes used to promote wound healing. The application of direct current is believed to enhance blood flow and cellular activity, potentially accelerating the healing process.
4. Functional Rehabilitation:
* Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES): FES is employed to stimulate specific nerves and muscles to produce functional movements. It is often used in rehabilitation for individuals with neurological conditions, such as spinal cord injuries or stroke, to improve mobility and restore functional activities.
5. Reducing Inflammation:
* Certain forms of electrotherapy may have anti-inflammatory effects, contributing to the management of conditions involving inflammation.
6. Nerve Stimulation:
* Interferential Current (IFC): IFC involves the use of intersecting medium-frequency electrical currents. It can be used for pain relief, muscle stimulation, and improving blood flow by creating a modulating interference effect.
7. Skeletal Pain and Osteoarthritis:
* Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy (PEMF): PEMF involves the use of electromagnetic fields to improve circulation and reduce pain and inflammation. It is sometimes used in the management of musculoskeletal conditions, including osteoarthritis.
8. Urinary Incontinence:
* Transvaginal Electrical Stimulation (TES) or Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): Electrical stimulation may be used to strengthen pelvic floor muscles and improve symptoms of urinary incontinence.
It's important to note that while electrical therapy can be beneficial for certain conditions, it may not be suitable for
everyone, and its effectiveness can vary from person to person. The specific type of electrical therapy, parameters of
stimulation, and treatment duration will depend on the individual's condition and the goals of therapy. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment approach for your specific needs.
FAQ
Q1. How can i order sample?
A1: Please contact us or click here:SEND INQUIRY, We will draft invoice for you.
Q2: Can you print my Logo on the products? How much cost for OEM?
A2: Yes, it is free based on 1000 pieces.
Q3: Can we get sample first before large order? How much cost?
A3: Sure, normally sample price is up 50% of 1000pcs price, but we can refund you after placing order.
Q4: What's your production time for the bulk order?
A4: Our production time is in 7-30 days for the mass order. And the sample will be sent in 3 days after received the payment.
Q5: How does your factory do regarding quality control ?
A5: 1) we set up very strict product quality control through DQE, SQE, FQC, and CQE these four aspects to manage 2) In addition,we have self-established laboratory inspection and invite official organization inspect.
Q6:Can we order on alibaba.com?
A6:Yes! Of course! We also we give you more discount if you order on alibaba.com.
Q7:Do you accept OEM/ODM?
A7:Yes! Of course! Most of our customers can make good profit through OEM/ODM.
A1: Please contact us or click here:SEND INQUIRY, We will draft invoice for you.
Q2: Can you print my Logo on the products? How much cost for OEM?
A2: Yes, it is free based on 1000 pieces.
Q3: Can we get sample first before large order? How much cost?
A3: Sure, normally sample price is up 50% of 1000pcs price, but we can refund you after placing order.
Q4: What's your production time for the bulk order?
A4: Our production time is in 7-30 days for the mass order. And the sample will be sent in 3 days after received the payment.
Q5: How does your factory do regarding quality control ?
A5: 1) we set up very strict product quality control through DQE, SQE, FQC, and CQE these four aspects to manage 2) In addition,we have self-established laboratory inspection and invite official organization inspect.
Q6:Can we order on alibaba.com?
A6:Yes! Of course! We also we give you more discount if you order on alibaba.com.
Q7:Do you accept OEM/ODM?
A7:Yes! Of course! Most of our customers can make good profit through OEM/ODM.
Q8:Could my company potentially serve as your regional or national agent?
A8:Certainly! We enthusiastically invite esteemed partners worldwide to collaboratively explore the market, fostering mutual benefit and
achieving win-win outcomes. Together, we aim to deliver high-quality products and services to our end consumers.
achieving win-win outcomes. Together, we aim to deliver high-quality products and services to our end consumers.
We Recommend
New Arrivals
New products from manufacturers at wholesale prices