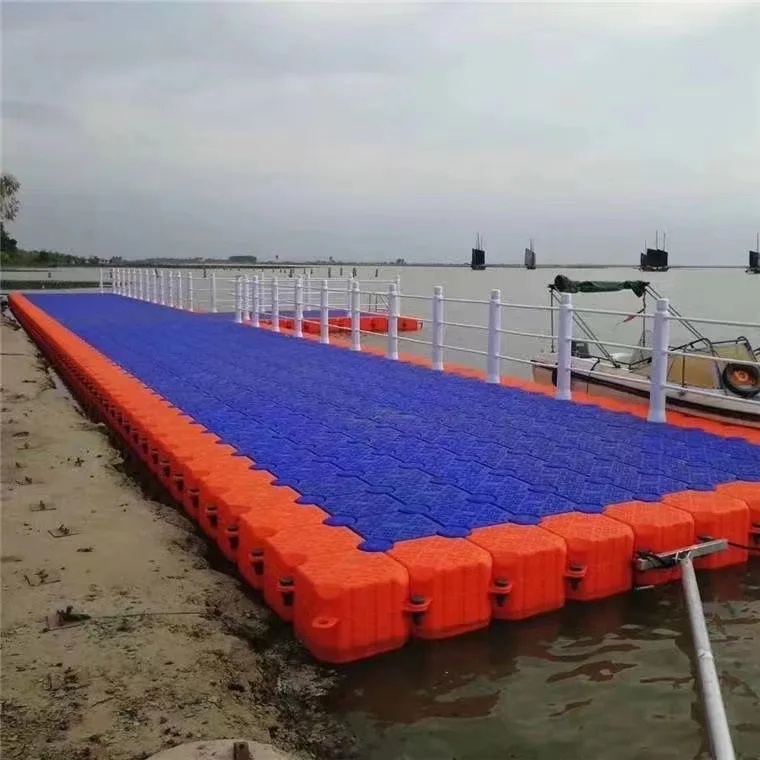
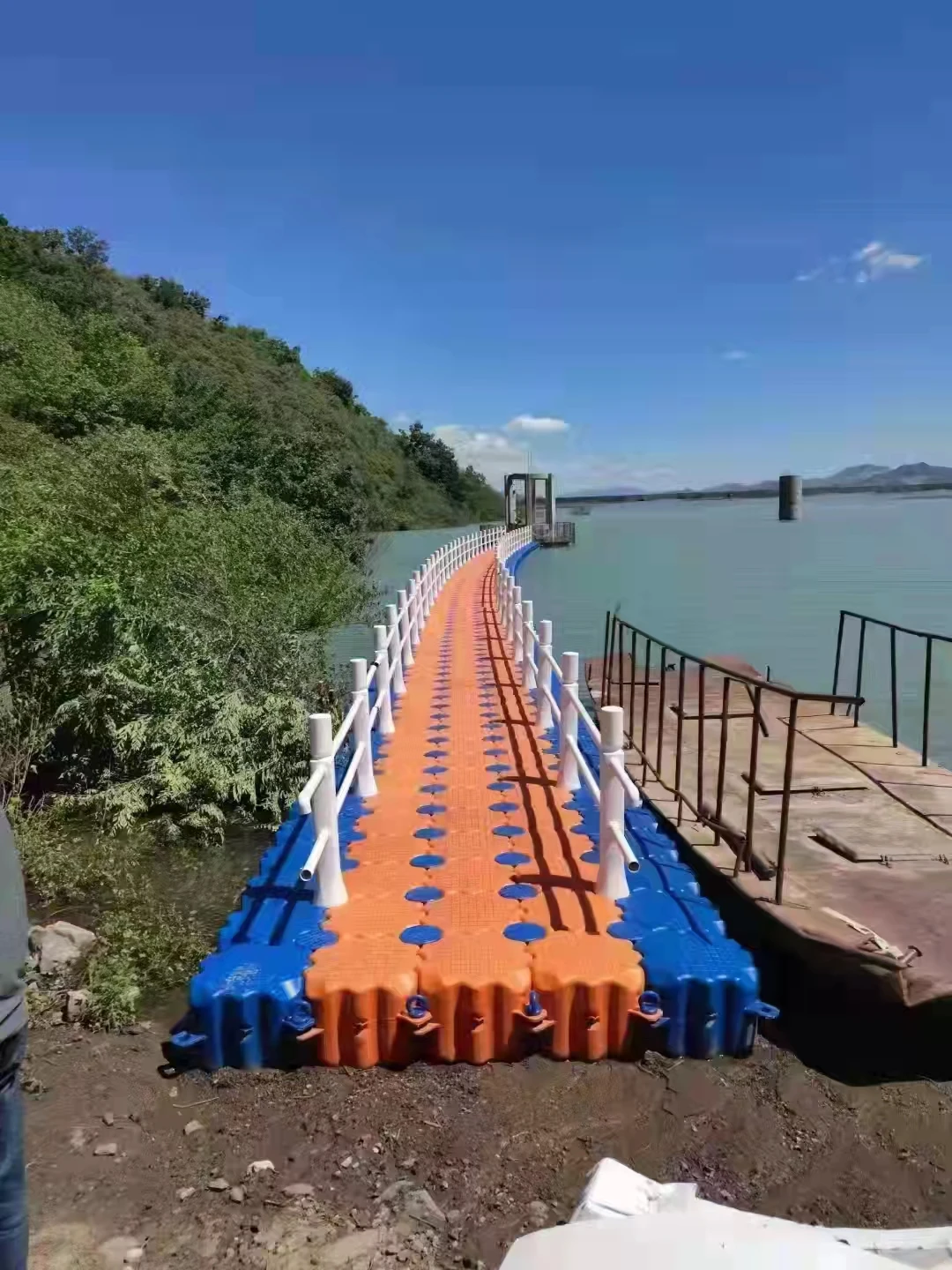
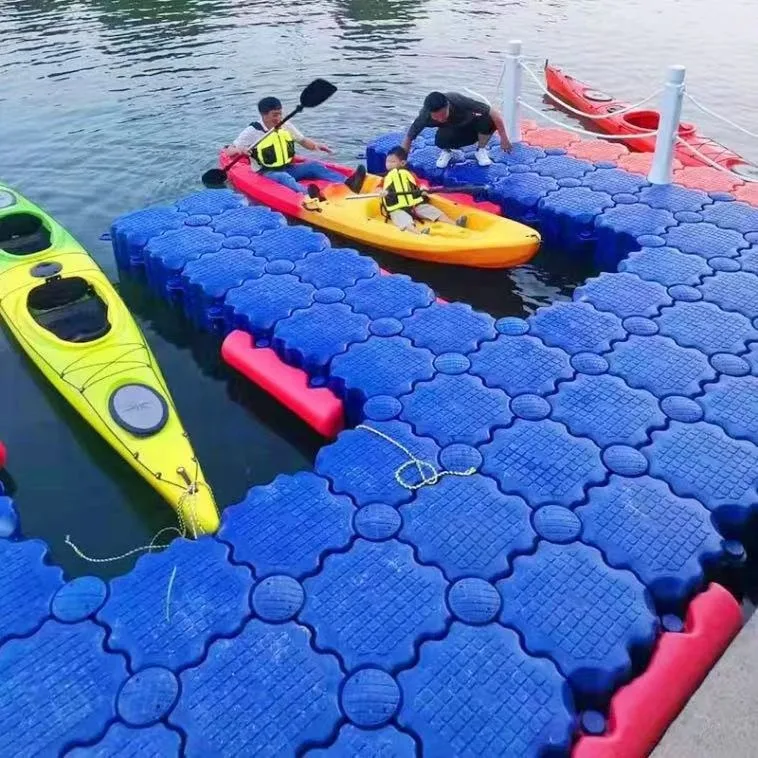
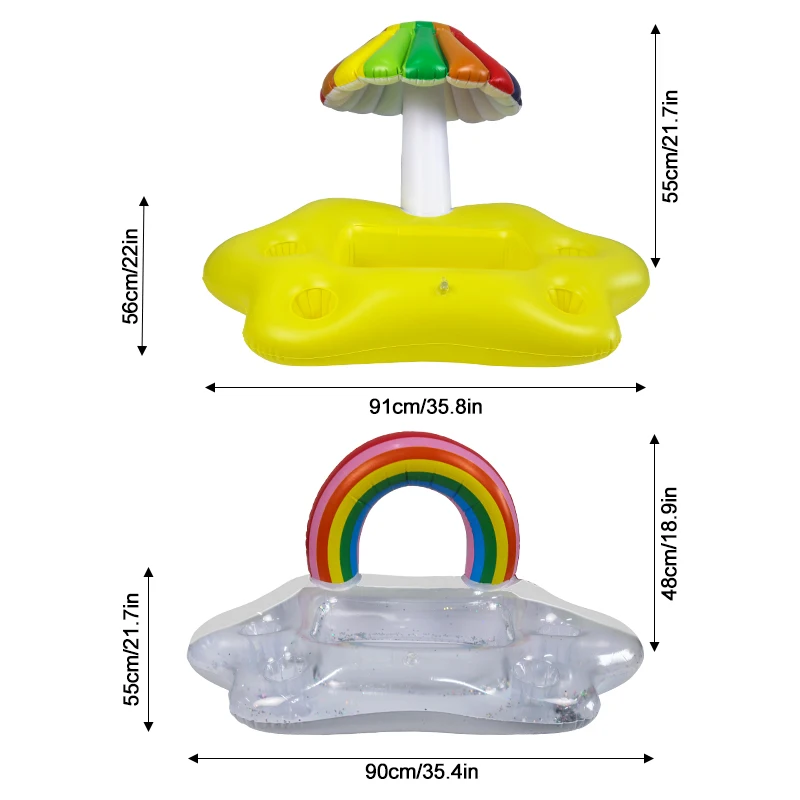
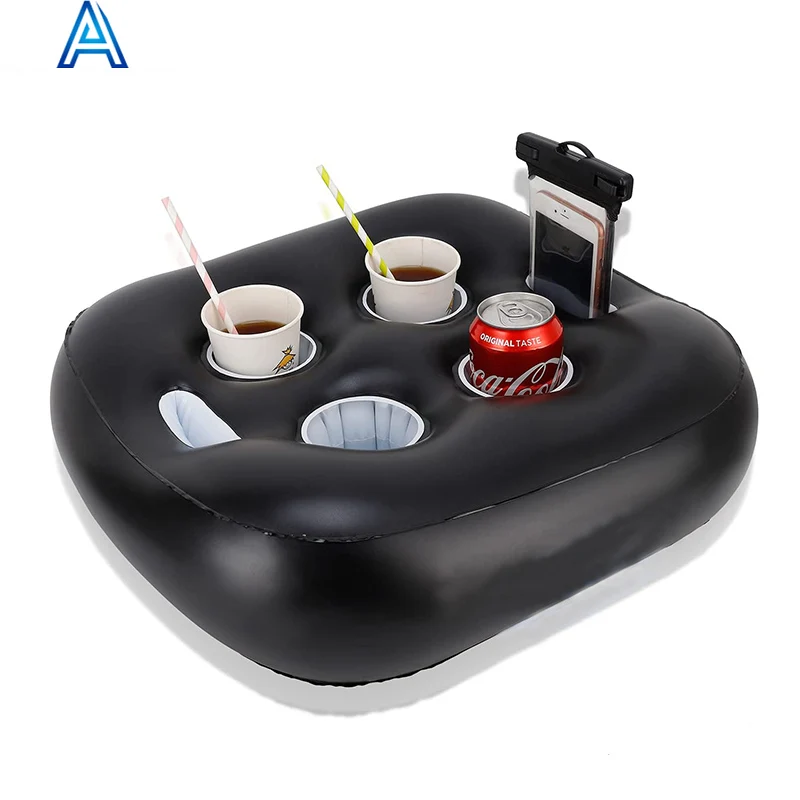
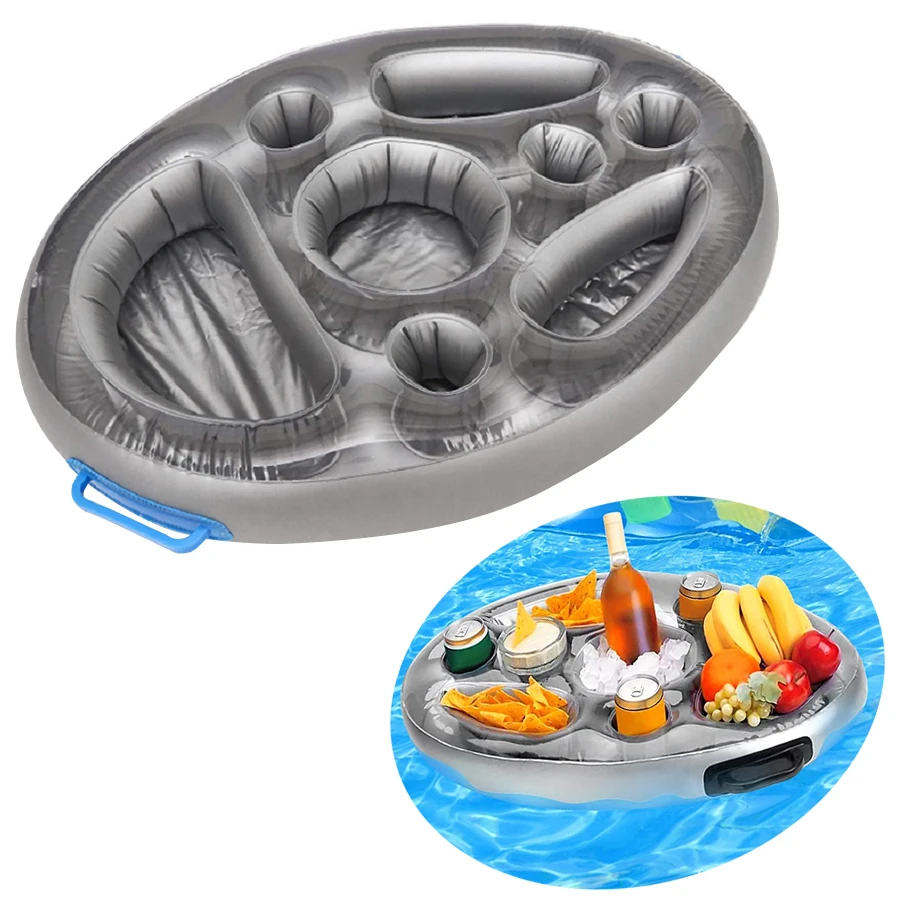
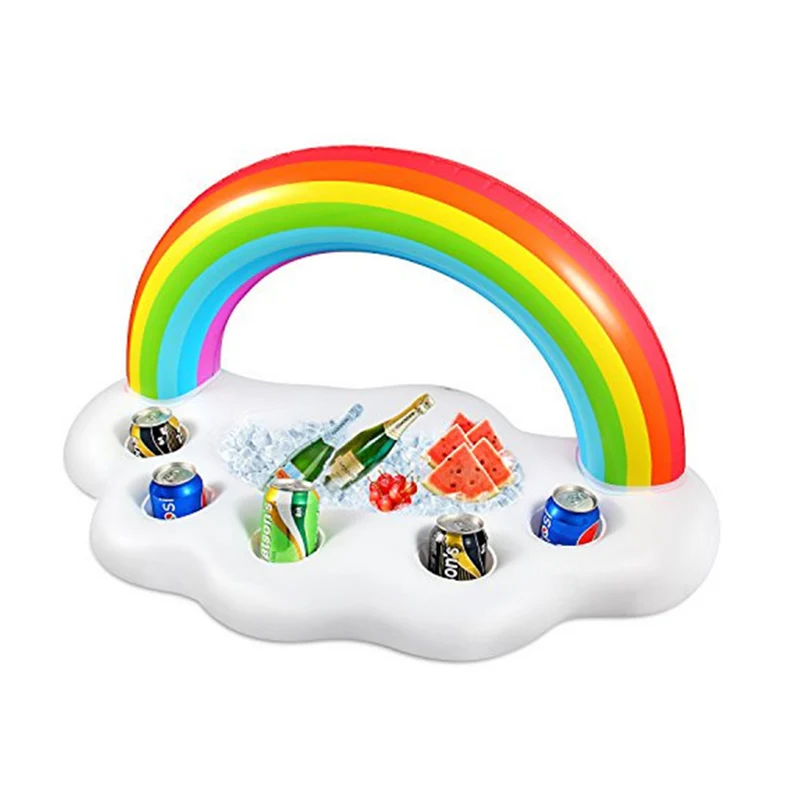
Пластиковая морская Плавающая Платформа плавающее ведро понтон коробка для отдыха
- Категория: >>>
- Поставщик: Damien New Energy Technology (wuhanshi) Co. Ltd.
Сохранить в закладки 1601206737720:
Описание и отзывы
Характеристики
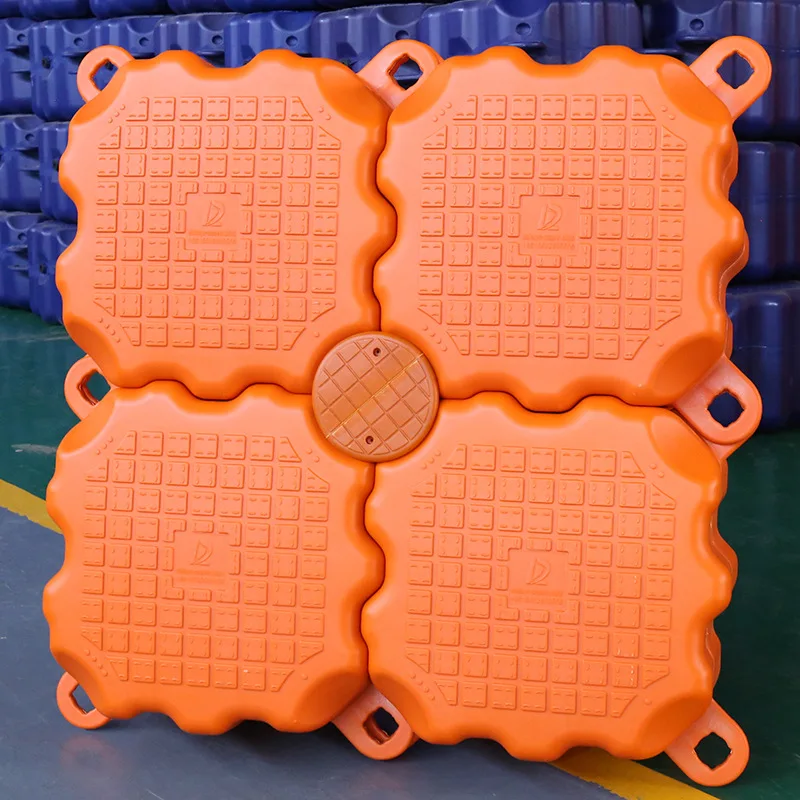
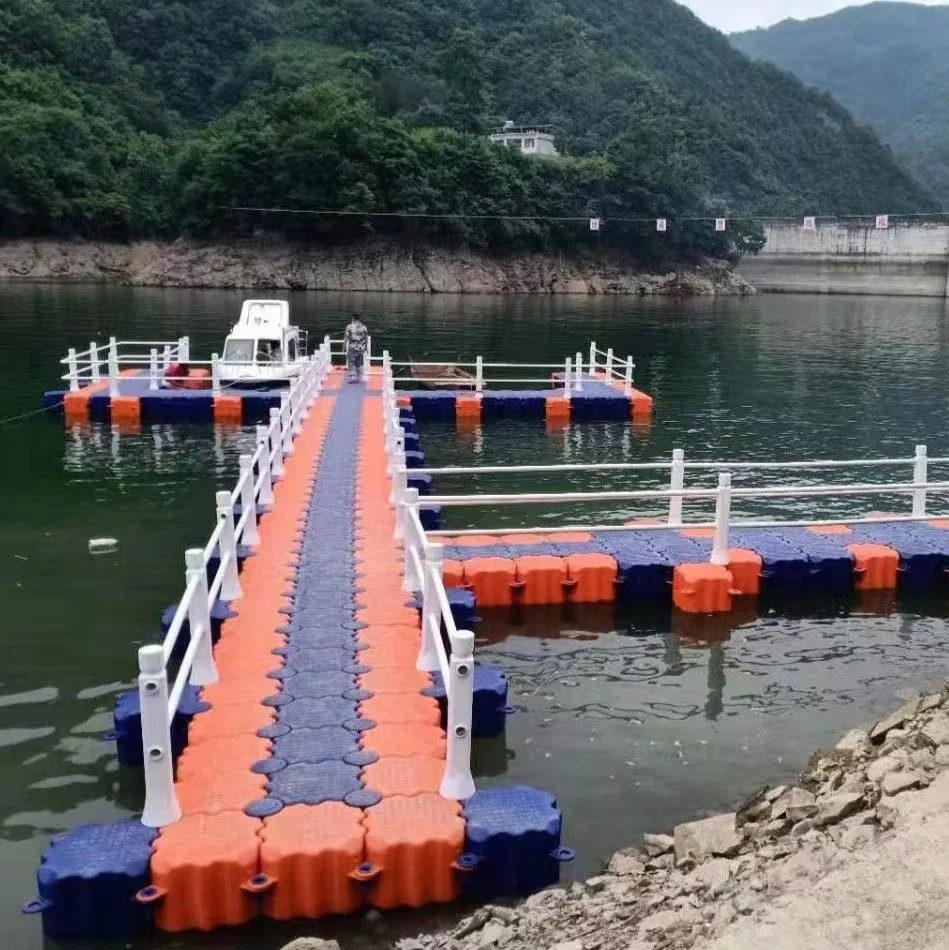
1. Flexible Design: Floating bridges come in various designs, tailored to fit the specific needs and preferences of the user. Whether it's a simple pedestrian walkway or a bridge capable of supporting heavy vehicles, there's an option for every requirement.
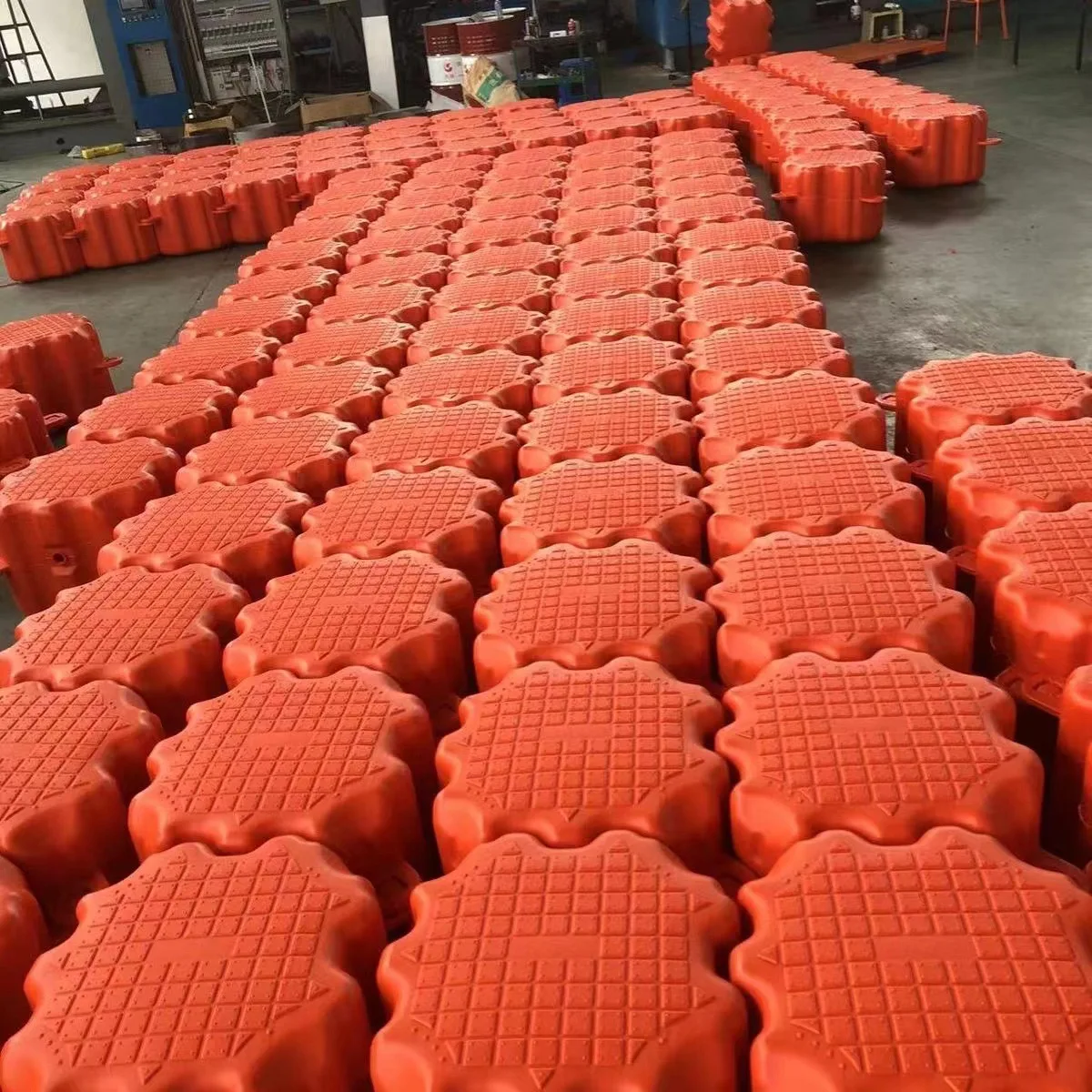
2. Durable Materials: Constructed from high-grade materials such as durable woods, corrosion-resistant metals, or advanced composite materials, these bridges ensure longevity and minimal maintenance.
3. Eco-Friendly: Floating bridges are often designed with an eco-conscious approach, minimizing impact on aquatic life and the environment. Their construction typically allows water to flow freely beneath them, maintaining natural water circulation and ecosystem health.
4. Easy Installation: Featuring modular components and straightforward assembly, installation of a floating bridge is generally quick and hassle-free. They can be deployed in areas where traditional bridge construction would be too challenging or costly.
5. Adaptable: These bridges are designed to adapt to fluctuations in water levels, ensuring they remain stable and functional regardless of the weather conditions or water currents.
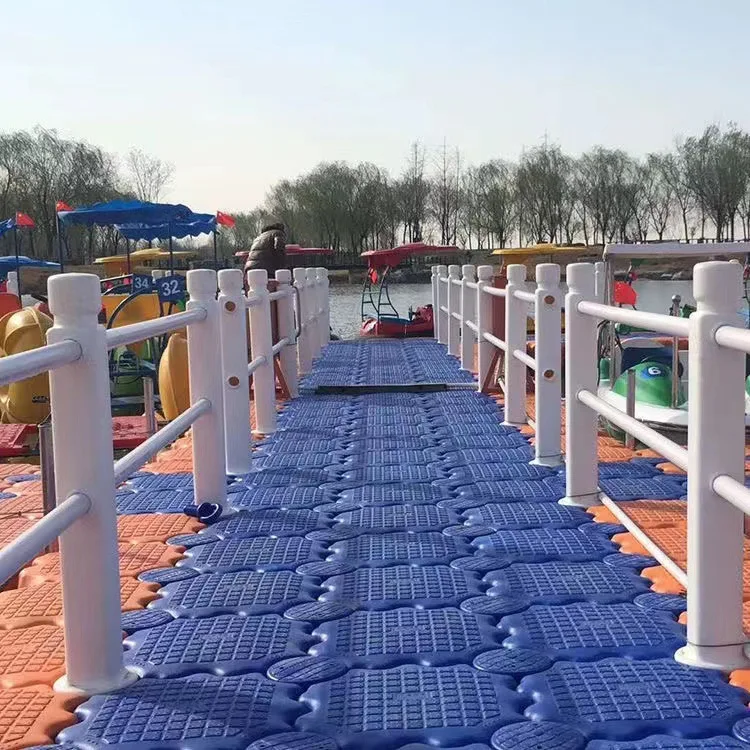
6. Versatile Applications: Suitable for a range of applications including recreational parks, private estates, resorts, and municipal projects, floating bridges serve both practical and recreational purposes.
7. Safe and Accessible: With features like non-slip surfaces, sturdy railings, and thoughtful access points, these bridges provide safe passage for all users, accommodating pedestrians, cyclists, and even some types of vehicles depending on the design.
8. Visually Appealing: A floating bridge adds a touch of elegance and contemporary style to any landscape. The aesthetics can be customized to blend seamlessly with the natural surroundings or to make a bold, modern statement.
9. Expansion Capabilities: As needs grow, many floating bridges offer the possibility to extend or modify the structure with additional sections or modules.
10. Minimal Environmental Footprint: Compared to fixed bridges, floating bridges often have less of an environmental footprint due to their minimal foundation requirements and the ability to install and remove them with less impact on the surrounding ecosystem.
In conclusion, floating bridges represent a smart and attractive solution for connecting waterfront properties, enhancing navigational experiences, and providing safe and enjoyable access to beautiful waterways. Their customizable nature ensures that no matter the context, there's a floating bridge that will meet your specific needs flawlessly.
1. Disassembly: Depending on the design and size of the floating bridge, it may need to be disassembled into smaller, more manageable sections for transport. This could involve taking apart modular components or folding elements to reduce their dimensions.
2. Packing Materials: Strong, durable materials such as wooden crates, metal containers, or heavy-duty plastic wrap might be used to securely package each section of the bridge. Shock-absorbent materials like foam inserts, cushioning wraps, and custom-cut Styrofoam may also be used to protect fragile parts.
3. Labeling and Marking: Each package is clearly labeled with handling instructions, such as "This Side Up," "Fragile," or "Keep Dry," to guide handlers during transportation. Markings may also indicate the order in which parts should be reassembled.
4. Loading: Sections are carefully loaded onto transportation vehicles, such as flatbed trucks or multi-modal transport carriers, using lifting equipment like forklifts or cranes. Care is taken to distribute weight evenly and secure the load to prevent shifting during transit.
5. Shipping: The method of shipping will depend on the distance to the destination and the size of the bridge components. Options include road transport, rail, or even shipment by sea for international destinations or very large structures.
6. Environmental Considerations: To protect the environment during transport, eco-friendly packaging materials may be used, and fuel-efficient transportation methods are preferred where possible.
7. Accompanying Documentation: All necessary paperwork, including bills of lading, shipping invoices, and any required export/import documents, are prepared to accompany the bridge sections throughout their journey.
8. Insurance: Given the value and complexity of floating bridges, transportation insurance is often secured to protect against loss or damage during transit.
9. Delivery and Offloading: Upon arrival at the destination, the sections are offloaded using appropriate equipment and procedures to avoid damage. Any necessary inspection is conducted to ensure all parts are intact and ready for assembly.
10. Assembly Instructions: Clear assembly instructions are provided to guide the reconstruction of the floating bridge on-site. In some cases, expert technicians from the manufacturer may be present to oversee the assembly process.
1. Design and Engineering Consultation: Professional services to design and engineer custom floating bridges that meet specific requirements, including factors such as weight capacity, dimensions, and environmental impact.
2. Installation Services: Expert installation is crucial for the proper functioning of a floating bridge. Services include on-site preparation, assembly, and placement of the bridge to ensure it is securely and correctly positioned.
3. Maintenance and Repairs: Regular maintenance services help to extend the lifespan of a floating bridge by addressing wear and tear issues, performing cleaning, and making necessary repairs.
4. Inspection Services: Periodic inspection services assess the structural integrity, safety features, and overall condition of the bridge to prevent potential problems and ensure compliance with regulations.
5. Upgrades and Modifications: As needs change or to improve functionality, services may include upgrading or modifying existing floating bridges, such as adding stability enhancements or expanding the bridge's length.
6. Mooring and Anchoring Systems: Services to install, adjust, or repair mooring and anchoring systems that keep the floating bridge stable and in place despite fluctuations in water levels or currents.
7. Accessibility Improvements: Services to improve accessibility for all users, including modifications like ramp installations, handrail additions, or surface treatments for better traction.
8. Environmental Assessment: Services to evaluate the environmental impact of the bridge and suggest ways to minimize its footprint, ensuring ecological sustainability.
9. Training and Information: Providing training to personnel who will manage and maintain the bridge, as well as offering user guides and safety information to the public.
10. Removal and Relocation Services: Should the need arise to relocate or remove the floating bridge, services are available to safely disassemble and transport the structure to a new location or remove it from the water body.
11. Customization Services: Services to customize the appearance or functionality of the bridge, such as adding decorative elements or integrating lighting and technology features.
12. Emergency Response: In case of accidental damage or extreme weather events, emergency response services are critical to quickly address any issues and minimize downtime.
1. Company Name: The first piece of information is the name of the company. This can usually be found on the company's official website, marketing materials, and business documentation.
2. Founding Date: The date when the company was established, which can provide insight into its experience and history in the industry.
3. Location: The geographical location or headquarters of the company, which may influence factors such as shipping costs, local regulations, and cultural considerations.
4. Services Offered: A detailed list of services provided by the company, including design, manufacturing, transportation, installation, maintenance, and any additional features like customization options.
5. Portfolio: A portfolio or case studies showcasing previous projects the company has completed, demonstrating their capabilities and providing examples of their work.
6. Certifications and Accreditations: Information about any certifications or accreditations the company holds, which attest to their adherence to quality standards, environmental practices, and safety regulations.
7. Contact Information: Details on how to get in touch with the company, including physical address, phone numbers, email addresses, and website URL.
8. Sustainability Practices: Information regarding the company's commitment to sustainability, eco-friendly materials, and green practices in their operations.
9. Client Testimonials: Customer reviews and testimonials that offer insights into the company's reputation and the quality of their work.
10. Awards and Recognitions: Any awards or recognitions the company has received for their work in the field of floating bridges or related industries.
11. Team and Management: Information about the company's key personnel, including engineers, project managers, and executives, along with their qualifications and experience.
12. Partnerships and Associations: Details of any partnerships or associations the company has with other businesses or professional organizations in the industry.
13. Social Media and Online Presence: Links to the company's social media profiles and other online platforms where they may share news, updates, and engage with clients and stakeholders.
14. Financial Information: For investors or large clients, financial information such as annual reports, revenue, and growth statistics could be relevant.
15. Guarantees and Warranties: Information regarding any guarantees or warranties the company offers on their products and services.
1. What is a floating bridge?
A floating bridge is a structure that spans over water and floats on the surface, typically anchored or moored in place to maintain its position. It provides a pathway for pedestrians, vehicles, or railway traffic to cross water bodies without the need for pillars or supports in the water.
2. How are floating bridges stabilized?
Floating bridges are stabilized using various methods such as mooring lines, anchoring systems, and sometimes even pontoons or floating piers depending on the design. These stabilization systems keep the bridge from moving due to currents, wind, or other forces.
3. What materials are used to construct floating bridges?
Floating bridges can be constructed from a variety of materials including steel, concrete, high-density polyethylene (HDPE), wood, and aluminum, depending on the design requirements and environmental conditions.
4. How long do floating bridges typically last?
The lifespan of a floating bridge depends on factors such as the quality of construction, the materials used, and how well it is maintained. With proper maintenance, a floating bridge can last for several decades.
5. Can floating bridges withstand harsh weather conditions?
Modern floating bridges are designed to be resilient and can often withstand harsh weather conditions, including strong winds and currents. However, extreme weather events may require additional stabilization or protective measures.
6. Are floating bridges safe in case of an emergency?
Floating bridges are designed with safety in mind and often include features such as railings, non-slip surfaces, and emergency access points. Proper maintenance and regular inspections are crucial to ensure safety at all times.
7. How often does a floating bridge need to be maintained?
Maintenance requirements vary depending on usage and environmental factors. Some floating bridges may need monthly checks, while others may require inspections every few years.
8. Can floating bridges be removed or relocated?
Yes, floating bridges can generally be disassembled and relocated if necessary. This makes them suitable for temporary installations or situations where the bridge needs to be moved due to changing circumstances.
9. Are there weight limits for using a floating bridge?
Most floating bridges are designed to support a specific maximum load. Exceeding this weight limit can compromise the structural integrity of the bridge and lead to safety hazards.
10. How much do floating bridges cost to build and maintain?
The cost of building and maintaining a floating bridge varies widely depending on size, materials, complexity, and location. Generally, floating bridges can be more economical than fixed bridges in deep or difficult-to-access waters.
11. Are floating bridges environmentally friendly?
Floating bridges can be designed to minimize environmental impact by using eco-friendly materials and construction techniques. Their placement on water also reduces the need for altering the landscape compared to traditional bridge construction.
12. Can any contractor build a floating bridge, or do you need specialized companies?
While some general contractors may have experience with floating bridges, it is often best to work with specialized companies that have expertise in designing, building, and maintaining these types of bridges.
13. How quickly can a floating bridge be installed?
Installation time frames vary depending on factors such as the size of the bridge, site conditions, and availability of materials and labor. Some prefabricated floating bridges can be installed relatively quickly, within a matter of days or weeks.
14. Do floating bridges require special permits or licenses?
Obtaining the necessary permits and licenses is essential for the construction and operation of a floating bridge. This process involves compliance with local, state, or national regulations and may include environmental impact assessments.
| Step | Action | Materials/Tools | Notes |
| 1 | Plan Design | Sketch, Measuring Tape,Pen&Paper | Determine length,width,anddesired load capacity |
| 2 | Gather Materials | Wood Planks,Floating Barrels or Pontoon Sections,Screws,Bolts | Choose durable wood such as cedar or treated lumber |
| 3 | Prepare Bridge Deck | Wood Planks,Saw,Drill,Sandpaper | Cut planks to size,sand edges for safety |
| 4 | Assemble Frame | Wood Planks,Screws,Drill | Connect the planks to form the deck frame |
| 5 | Attach Floating Supports | Pontoon Sectiions,Bolts,Wrench | Secure the pontoons to the underside of the deck |




Похожие товары
Лидер продаж, надувные бутылки, ведро для пива, держатели для облачных напитков, флоат, салат, фруктовый поднос
Надувная подставка для фруктов из ПВХ
2-функциональная виниловая Экологически чистая ПВХ надувная бутылка для бассейна, поднос для воды, поднос для пивной колы, поднос для напитков, держатель для мобильного телефона
Лидер продаж, надувные поплавки для взрослых, надувные поплавки для бассейна, надувные поплавки
Надувной держатель для напитков с 8 отверстиями
Высокое качество надувной плавающий поднос держатель для напитков бутылка пива ведро кулер ПВХ Радуга облака сервировочный поднос
Надувной Аэро-стул для передней палубы яхты, портативный Аэро-надувной пляжный диван для надувной док-станции
Новые поступления
Новинки товаров от производителей по оптовым ценам